Speed is Scalar or Vector
Velocity on the other hand is a vector quantity. See Speed and Velocity to learn more.
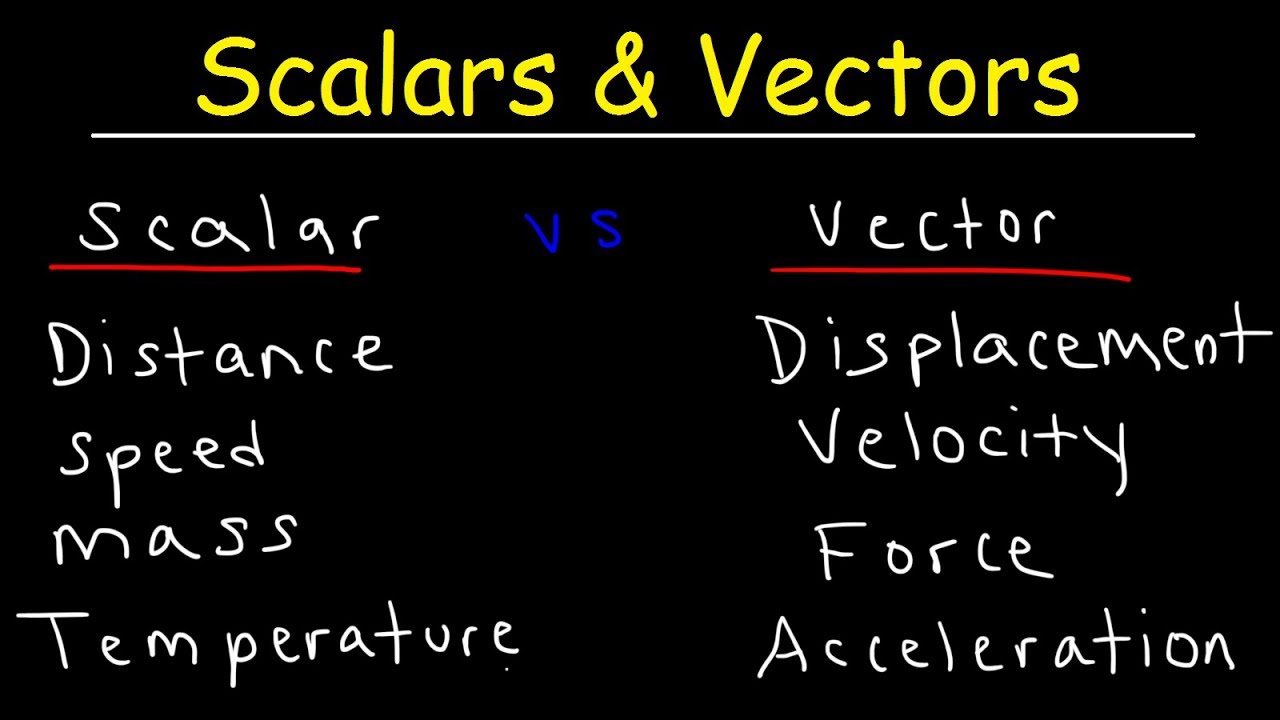
A scalar quantity is a physical quantity with only magnitudes such as mass and electric charge.

. Speed is defined as the distance travelled by an object in a unit of time. You can index into a timetable by row time and variable. Given a point of the manifold a vector field.
On the other hand a vector quantity is a physical quantity that has both magnitudes and directions like force. Its velocity is 50 mph in the northeast direction. Speed is how fast something moves.
When any vector is divided by its own magnitude the result is a vector with a magnitude of 1 which is known as a normalized vector. Vcavcbvcbvca This law is also called the parallelogram law as illustrated in. The average speed is the distance a scalar quantity per time ratio.
Vector processing ignores the overhead caused due to the loops while operating on an array. A vector operand has several scalar data elements. It is a direction-aware quantity.
Instead vector graphics are comprised of vertices and paths. If a normalized vector is multiplied by a scalar then the magnitude of the result will be equal to that scalar value. In Physics we often use the terms force speed velocity and work and these quantities are classified as a scalar or vector quantities.
So c is a vector it has magnitude and. The vector projection is the vector that is produced when one vector is just divided into two vectors. Although a vector has magnitude and direction it does not have position.
Accepts input of following types. It doesnt consider the direction of the object ie it has only magnitude. The scalar and vector variables may be chosen from this datasets arrays.
The commutative law which states the order of addition doesnt matter. It is a vector quantity. The magnitude of the force indicates the strength while if we talk about the magnitude of velocity it indicates the speed.
Defined in a neighborhood of p. For a scalar function f and vector field v the covariant derivative coincides with the Lie derivative and with the exterior derivative. As we have now understood the difference between scalar and vector let us now discuss more scalar and vector.
But saying he runs 9 kmh Westwards is a velocity. We can then add vectors by adding the x parts and adding the y parts. However talking about velocity velocity is defined as the rate of change of displacement.
You can reference variables and the vector of row times using names. Is the function that associates with each point p in the common domain of f and v the scalar. This is how speed is called a scalar quantity.
The vector 8 13 and the vector 26 7 add up to the vector 34 20. An example of a scalar quantity is temperature. U V j V.
The direction of a vctor V is the unit vector U parallel to V. By definition speed is the scalar magnitude of a velocity vector. Vector algebra is useful to find the component of the force in a particular direction.
Speed is ignorant of direction. A car going down the road has a speed of 50 mph. To distinguish them from.
Is a vector field on the covariant derivative. Scalar triple product of vectors is the dot of one vector with the cross product of the other two vectors. Therefore the total speed of the object ie the magnitude of the velocity vector is sqrt20220220sqrt2 miles per hour relative to the ground.
Are scalars so they have no direction. A scalar quantity is one that has only magnitude but no direction. This is useful when the direction of a force is constant but the strength is controllable eg.
If any two vectors in a scalar triple product are equal then the. Addition of vectors satisfies two important properties. Speed eg 8 metres per second ms density eg 1500 kilograms per metre cubed kgm 3 Calculations involving scalar quantities Adding scalars.
To index into a timetable use smooth parentheses to return a subtable or curly braces to extract the contents. Hen ce vector processors have a pipelined structure. It is typically represented by an arrow whose direction is the same as that of the quantity and whose length is proportional to the quantitys magnitude.
The sum of scalar quantities can be found by. That is as long as its length is not changed a vector is not altered if it is displaced. The dataset must contain a field array AttributeMode AttributeMode This property determines whether the computation is to be performed on point-centered or cell-centered data.
Vector algebra is used to find the interplay of two or more quantities in physics. The average velocity is the displacement a vector quantity per time ratio. Vector data is not made up of a grid of pixels.
Another example is mass and weight. So this is how vector processing allows parallel operation on the large arrays and fasten. It can get very confusing when the terms are used interchangeably.
The remainder of this lesson will focus on several examples of vector and scalar quantities distance displacement speed velocity and acceleration. As we proceed through other units at The Physics Classroom Tutorial and become. Vector U is a vector of length 1.
The difference between scalar and vector quantities is an important one. The temperature at a given point is a single number. Along with this it gives you direction also.
Q the vector from P to Q is denoted PQ. 1 The values is an enumeration of the following. Speed is a scalar quantity it is the rate of change in the distance travelled by an object while velocity is a vector.
Weight is a force which is a vector and has a magnitude and direction. B Given two points P. Because cartographers use these symbols to represent real-world features in maps they often have to decide based on the level of detail on the map.
So it is merely a number accompanied by the corresponding unit. In vectors that are divided one vector is parallel to the other vector and another vector is perpendicular to the. Saying Ariel the Dog runs at 9 kmh kilometers per hour is a speed.
The three basic symbol types for vector data are points lines and polygons areas. The sum or resultant V W of two vectors V and W is the diagonal of the parallelogram with sides VW. On the other hand velocity is a vector quantity.
As you proceed through the lesson give careful attention to the vector and scalar nature of each quantity. The row times of a timetable are datetime or duration values that label the rows. For example length mass duration speed etc.
Velocity is speed with a direction. Speed being a scalar quantity is the rate at which an object covers distance. A vector is often written in bold like a or b so we know it is not a scalar.
Some examples of scalar quantities in physics are mass charge volume time speed pressure and electric potential at a point inside a medium. The vector a is broken up into the two vectors a x and a y We see later how to do this Adding Vectors. Vector in physics a quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
A vector instruction needs to perform the same operation on the different data set.

Scalar And Vector Quantities Physics Lessons Physics Classroom Learn Physics

Vector Versus Scalar Physics Data Science Learning Physical Science Lessons

Vector Vs Scalar New Science Poster

Is Velocity Scalar Or Vector The Best Vector 2017 Science Notes Physics Poster Learn Physics

Vector Vs Scalar State Whether Each Introduction To Physics Physics Classical Mechanics

Comments
Post a Comment